In some cases,more than one exception could be raised by a single piece of code .To handle this type of situation ,you can specify two or more catch clauses ,each catching a different type of exception .When an exception is thrown each catch statement is inspected in order and the first one whose type matches that of the exception is executed .After one catch statement executes ,the others are bypassed and execution continues after the try/catch block
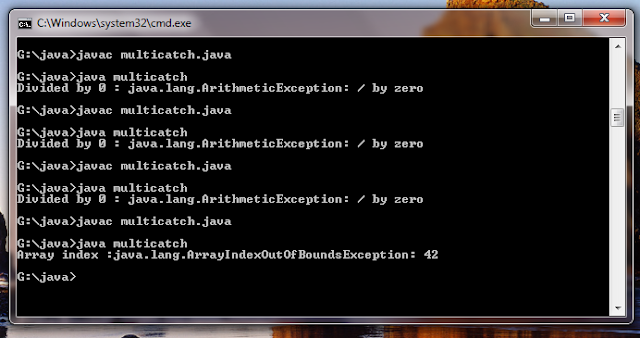
The program will cause a division by Zero exception if it is started with no command line parameters ,since a will equal zero . it will suvive the division if you provide a command line arguament setting a to something larger than zero .But it will cause an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ,since the int array c has a length of 1.yet the program attempts to assign a value to c[42].
When you use multiple catch statements it is important to remeber that exception subclasses must come before any of their superclasses.This is because a catch statement that uses a superclass will catch exceptions of that type plus any of its subclasses ,Thus a subclass would never be reached if it came after its superclass further in java unreachable code is an error.
class multicatch
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
try
{
int c[]={1};
c[42]=99;
int a=0;int b=42/a;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("Divided by 0 : "+e);
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ae)
{
System.out.println("Array index :"+ae);
}
}
}
The program will cause a division by Zero exception if it is started with no command line parameters ,since a will equal zero . it will suvive the division if you provide a command line arguament setting a to something larger than zero .But it will cause an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ,since the int array c has a length of 1.yet the program attempts to assign a value to c[42].
When you use multiple catch statements it is important to remeber that exception subclasses must come before any of their superclasses.This is because a catch statement that uses a superclass will catch exceptions of that type plus any of its subclasses ,Thus a subclass would never be reached if it came after its superclass further in java unreachable code is an error.
class multicatch
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
try
{
int c[]={1};
c[42]=99;
int a=0;int b=42/a;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("Divided by 0 : "+e);
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ae)
{
System.out.println("Array index :"+ae);
}
}
}
Output
Array index: java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundEception :42
0 comments:
Post a Comment